Marketing Canvas - Positioning
About the Marketing Canvas Method
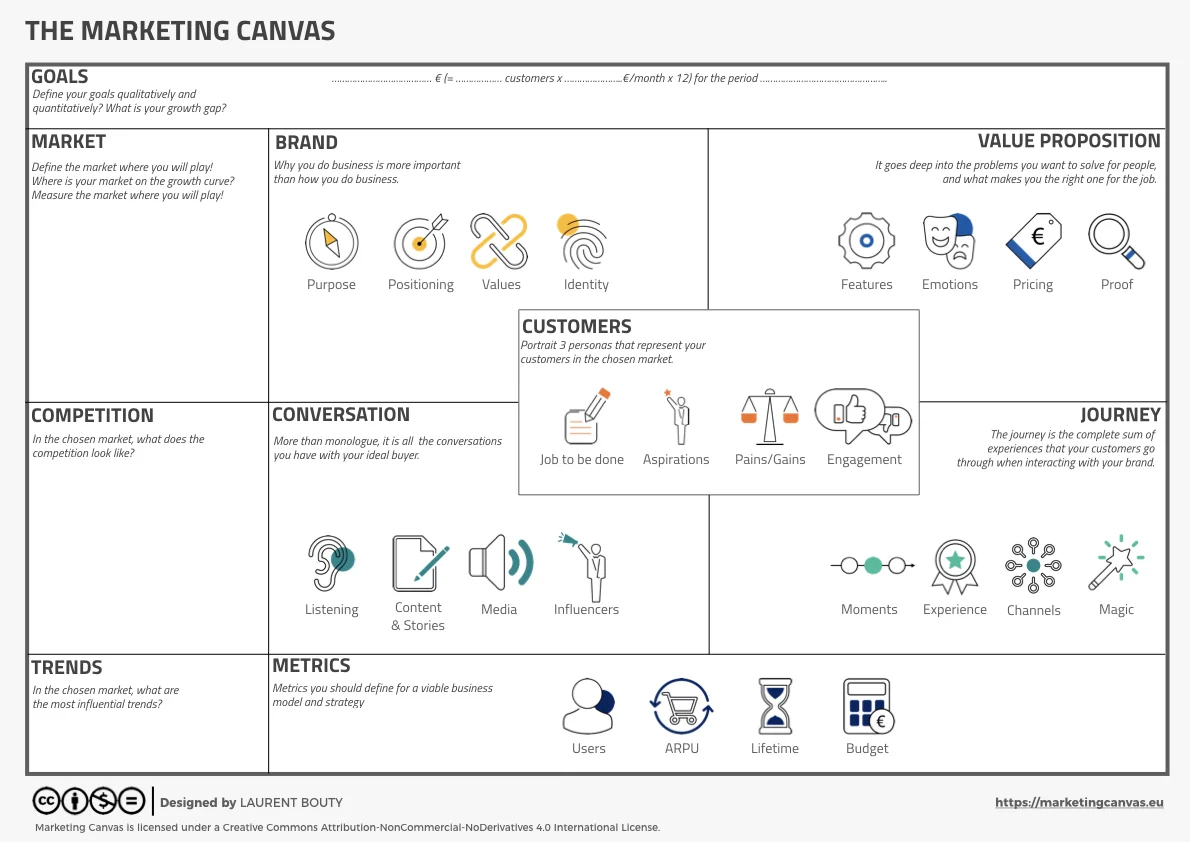
This article covers dimension 220 — Positioning, part of the
Brand meta-category. The Marketing Canvas Method structures
marketing strategy across 24 dimensions and 9 strategic archetypes.
Full framework reference at
marketingcanvas.net →
·
Get the book →
In a nutshell
The Positioning sub-dimension in the Marketing Canvas helps define how a brand is perceived by its target audience. Effective positioning differentiates the brand from competitors, conveys unique value, and aligns with the needs and aspirations of its customers. A strong positioning strategy shapes the brand’s identity, supporting its place in the market and creating a meaningful emotional connection with its audience.
For example, a company like Green Clean might position itself as “the eco-friendly cleaning solution prioritizing family health and environmental impact,” highlighting its unique benefits and commitment to sustainability.
Introduction
The Positioning sub-dimension is an essential element of the Brand category in the Marketing Canvas. It establishes how a brand is perceived compared to competitors, how it fulfills customer expectations, and the unique values it communicates. Positioning is more than a slogan or tagline; it’s an overall strategy that guides a brand’s communications, customer experience, and market identity.
A well-defined positioning strategy helps a brand build loyalty, stay relevant, and stand out in a crowded marketplace.
What is positioning?
Positioning represents the perception a brand creates in the minds of its target audience. It reflects what makes the brand unique and why customers should choose it over competitors. Successful positioning resonates with customers by emphasizing specific benefits and values that align with their needs and aspirations.
For instance, Green Clean’s positioning might emphasize its commitment to “safe and sustainable cleaning solutions,” appealing to customers who prioritize health and environmental responsibility. By clearly conveying its unique benefits, Green Clean establishes a distinct identity within the cleaning products market.
Positioning: an in-depth perspective
Positioning goes beyond words; it shapes a brand’s identity and influences how customers experience and remember it. A strong positioning strategy aligns with the brand’s core mission, resonates with its target audience, and clearly differentiates it from competitors.
For example:
Differentiation: Green Clean’s positioning emphasizes its eco-friendly values, setting it apart from traditional cleaning brands.
Relevance: By aligning with customer priorities like health and sustainability, Green Clean’s positioning appeals directly to its target audience, strengthening loyalty and trust.
When positioning is effectively implemented, customers can easily understand and identify with the brand’s unique purpose and value.
Positioning Types: Leader, Challenger, Disruptor
The 'Positioning' in the Marketing Canvas proposes three potential roles: Leader, Challenger or Follower, and Game Changer or Disruptor.
Leader Brand: This is the choice of mass consumers, often at the risk of losing early brand enthusiasts. These brands enjoy substantial mindshare and market share. They represent the category and dominate the space. For example, in the clean energy sector, a leader might be a company like NextEra Energy, known for its extensive wind and solar power production.
Challenger or Follower Brand: These brands turn leaders' strengths into their weaknesses. Recognized as viable alternatives to Leader brands, Challengers often leverage differentiation or provide cost-effective solutions. In the context of green energy, a challenger brand could be a new renewable energy startup offering innovative, localized energy solutions that large-scale leaders cannot provide.
Game Changer or Disruptor Brand: Disruptor brands find a 'Blue Ocean' market space for themselves, using a unique product, distribution channel, target market, or price point. For example, a clean energy disruptor might be a brand that creates a new technology for harnessing renewable energy, redefining the industry norms.
Translating positioning into action
Positioning is only effective when consistently applied across all aspects of a brand, from marketing and customer service to product development. Ensuring that all brand elements reflect its positioning strengthens its identity and reinforces customer expectations.
Questions to consider:
How does your brand’s positioning clearly differentiate it from competitors?
What unique value does your positioning highlight for customers?
Does your positioning align with customer values and long-term expectations?
Are you consistently reinforcing your positioning across all brand touchpoints?
Statements for self-assessment
For a comprehensive evaluation of your understanding and application of the Purpose concept, rate your agreement with the following statements on a scale from -3 (completely disagree) to +3 (completely agree):
You have a well defined and clearly formulated brand positioning.
Your brand positioning is very relevant in the company's current and future context, addressing all the influencing trends.
Your brand positioning is attainable taking into account resources and limitations.
Your brand positioning is aligned with your company culture and capabilities.
Every aspect of your positioning is in line with the concept of sustainability
Interpretation of the scores
Negative scores (-1 to -3): Negative scores suggest that you disagree or strongly disagree with the statements, indicating a lack of clarity, relevance, or alignment in your brand’s positioning. This can result in a weak brand identity, limited customer loyalty, and minimal differentiation from competitors.
A score of zero (0): A neutral score reflects uncertainty or incomplete understanding of your brand’s positioning. While some positioning elements may be present, they lack cohesiveness or fail to fully resonate with the target audience. Further refinement and alignment are necessary to strengthen the positioning.
Positive scores (+1 to +3): Positive scores indicate that you agree or strongly agree with the statements, suggesting a clear, well-defined positioning that aligns with customer expectations, differentiates the brand, and consistently communicates its unique value. This strengthens customer loyalty and brand perception.
Case Study: Green Clean’s positioning
Misaligned Understanding (-3, -2, -1): Green Clean lacks a clear, distinct positioning strategy, failing to differentiate itself from other cleaning brands. Without focused positioning, customers see Green Clean as generic and have little reason to choose it over competitors, leading to a diluted brand identity.
Surface Understanding (0): Green Clean has a general positioning related to eco-friendliness but does not fully leverage it to create a distinct identity. Although it acknowledges the importance of sustainability, the positioning is vague or inconsistently communicated, which limits customer engagement and weakens brand perception.
Deep Understanding (+1, +2, +3): Green Clean has a strong, clearly defined positioning centered on safe and sustainable cleaning solutions. This positioning is consistently reflected across all marketing, customer interactions, and product offerings. By emphasizing health and environmental responsibility, Green Clean builds a unique identity that resonates with eco-conscious customers, distinguishing it from conventional brands.
Conclusion
Positioning is essential for defining a brand’s unique place in the market and ensuring it resonates with the target audience. A well-defined and consistently communicated positioning strategy enables brands to stand out, build loyalty, and create emotional connections. By defining and reinforcing its unique value, a brand can establish a strong, memorable identity in the minds of its customers.
Sources
DKY, 2016, https://dkyinc.com/2016/06/brand-strategy-leader-vs-challenger
Beloved Brands, https://beloved-brands.com/2018/04/11/disruptor-challenger/