BLOG
A collection of article and ideas that help Smart Marketers to become Smarter
Marketing Canvas - Engagement
Explore the essence of customer engagement with the Marketing Canvas Method. Discover how to measure and improve it with tools like NPS. Drive your business growth by turning customer engagement into your success accelerator.
Last update: 30/10/2024
In a nutshell
Engagement sub-dimension in the Marketing Canvas focuses on how effectively a business can capture and sustain the interest of its customers. Engagement goes beyond simply attracting attention; it requires creating lasting connections that drive active participation, loyalty, and advocacy. By understanding the factors that influence engagement, companies can design marketing strategies that foster meaningful interactions with their audience.
For example, an eco-friendly cleaning brand like Green Clean might engage customers by sharing content on sustainable living, offering loyalty rewards, or creating a community around environmental responsibility. This level of engagement helps deepen customer relationships and build a strong brand community.
Introduction
Engagement sub-dimension, within the Customer category of the Marketing Canvas, focuses on building and maintaining a connection with customers that drives ongoing interest and involvement. This connection is based on a combination of communication, value delivery, and emotional resonance, which are key to keeping customers engaged over the long term.
While Pains and Gains look at addressing customer frustrations and needs, Engagement emphasizes the importance of continuous, active interaction, aiming to build loyalty and foster a community around the brand.
In the marketing canvas
The Marketing Canvas is a powerful tool for entrepreneurs and non-marketers to build a robust marketing strategy. It consists of six meta-dimensions, each with four sub-dimensions, for a total of 24 sub-dimensions defining your Marketing Strategy. One of these sub-dimensions is “Engagement”, which falls under the CUSTOMER category.
What is engagement?
Engagement represents the emotional and behavioral commitment a customer has with a brand. This commitment might manifest as repeat purchases, sharing positive feedback, participating in brand events, or advocating for the brand. Engaging customers requires understanding their interests, delivering consistent value, and encouraging them to participate in a shared experience with the brand.
For example, Green Clean might engage its eco-conscious customers by:
Providing resources on reducing household waste.
Offering loyalty rewards for repeat purchases of eco-friendly products.
Organizing community events focused on environmental sustainability.
Engagement is essential for building a brand community and transforming customers into advocates.
Engagement: an in-depth perspective
Engagement is about maintaining a two-way interaction between a brand and its customers. It requires businesses to understand what motivates their customers to stay connected and to respond proactively to their interests and feedback.
For example:
Active Engagement: A customer who frequently interacts with Green Clean’s social media content or attends brand-hosted events feels a personal connection with the company’s mission.
Passive Engagement: A customer may use Green Clean’s products without actively engaging with the brand’s content or events. Converting passive engagement into active participation can enhance loyalty and increase brand advocacy.
Understanding the depth and type of customer engagement helps businesses tailor their approaches to meet the specific preferences of their audience.
Tools for engagement: the NPS methodology
The NPS methodology segments customers into three groups based on their level of engagement: Promoters, Passives, and Detractors. Promoters are champions of your brand who will actively recommend your products or services. Detractors, on the other hand, may express dissatisfaction and may discourage others from interacting with your company. Passives fall in-between; they are neither actively promoting nor detracting from your brand.
The usefulness of NPS doesn't stop at categorizing customers. When you compare your NPS score with your competitors', you can gain valuable insights into your brand's standing in the market. This comparison can be achieved through an NPS study of your competitor's customer base or the broader market.
Translating engagement into action
To foster deep and lasting engagement, businesses should prioritize consistent, value-driven interactions that resonate with customer interests. Encouraging feedback, providing valuable resources, and fostering a sense of community can transform passive customers into loyal, actively engaged brand advocates.
Questions to consider:
How do your customers prefer to engage with your brand?
What types of content or interactions resonate most with your audience?
How can you create opportunities for customers to share their experiences and become advocates?
Statements for self-assessment
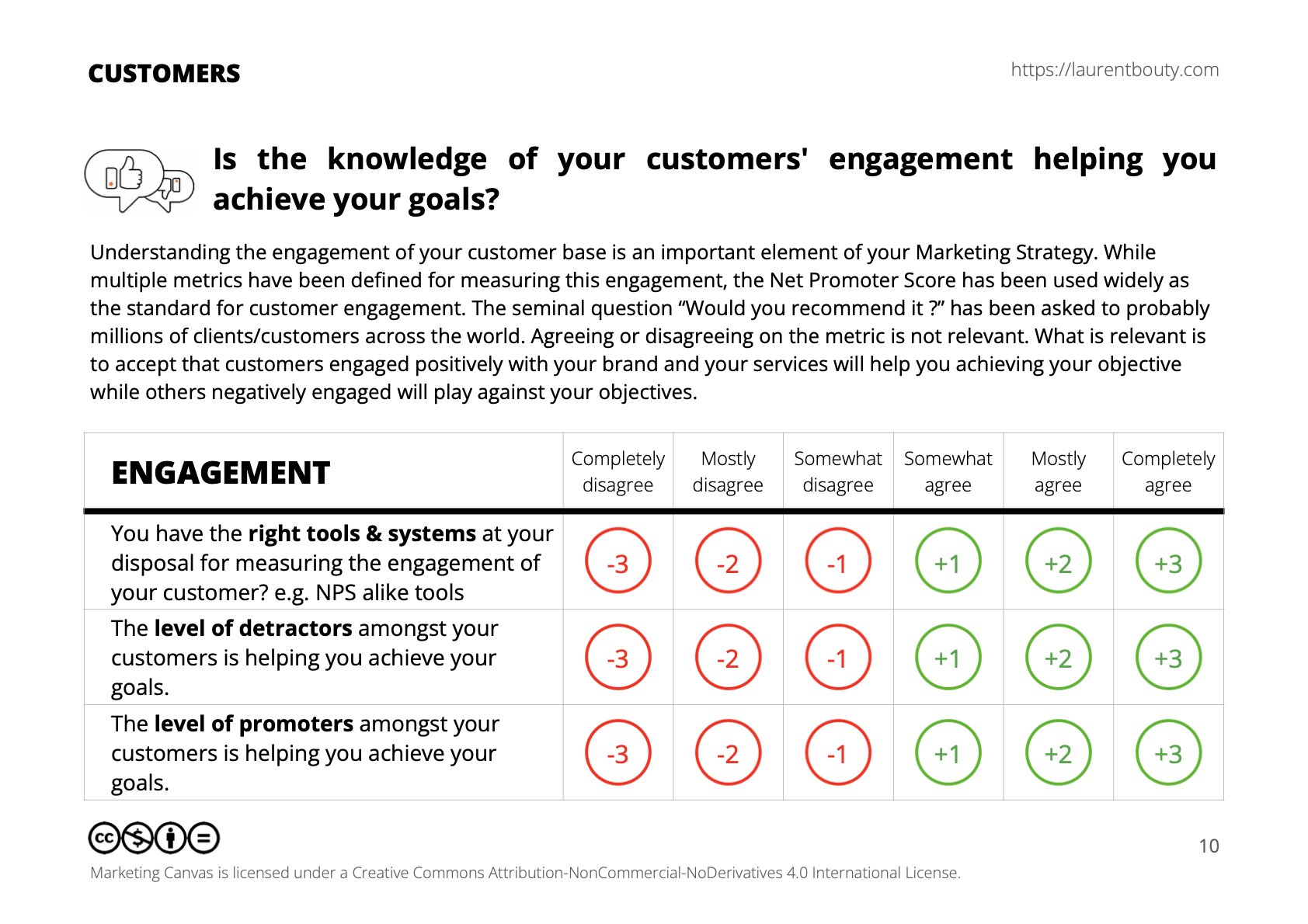
For a comprehensive evaluation of your understanding and application of the Engagement concept, rate your agreement with the following statements on a scale from -3 (completely disagree) to +3 (completely agree):
You have the right tools & systems at your disposal for measuring the engagement of your customer? e.g. NPS alike tools
The level of detractors amongst your customers is helping you achieve your goals.
The level of promoters amongst your customers is helping you achieve your goals.
You understand the role of sustainability in customer engagement and have aligned your strategies accordingly.
Marketing Canvas Method - Customers - Engagement by Laurent Bouty
Marketing Canvas Method - Customers - Engagement & Sustainability by Laurent Bouty
Interpretation of the scores
Negative scores (-1 to -3): Suggest significant gaps in measuring and managing engagement. Detractors may be impacting your goals negatively, and promoters may not be effectively leveraged. Engagement strategies may lack alignment with sustainability principles.
A score of zero (0): Reflects a functional but under-optimized engagement strategy. While tools and systems may exist, their use may not be systematic or effective, limiting overall impact.
Positive scores (+1 to +3): Indicate a strong engagement strategy. Detractors are addressed effectively, promoters are empowered, and engagement efforts align with sustainability, driving loyalty and advocacy.
Case study: Green Clean’s Engagement strategy
Misaligned understanding (-3, -2, -1): Green Clean lacks the tools to measure engagement and struggles to address customer dissatisfaction. Detractors outnumber promoters, harming the brand’s reputation, while sustainability efforts are absent from its engagement strategy.
Surface understanding (0): Green Clean uses basic tools like surveys but lacks a cohesive approach to managing detractors and empowering promoters. Sustainability is a peripheral concern, limiting its appeal to eco-conscious customers.
Deep understanding (+1, +2, +3): Green Clean leverages NPS and behavioral data to track engagement effectively. It proactively resolves detractor concerns, encourages promoters to share positive reviews, and integrates sustainability into its messaging, fostering strong customer relationships.
Conclusion
The Engagement sub-dimension highlights the importance of measuring and optimizing customer interactions to build loyalty, encourage advocacy, and align with sustainability. A thoughtful engagement strategy ensures that detractors are addressed, promoters are empowered, and the brand remains relevant in an eco-conscious market.
Sources
Harvard Business Review, 2003, https://hbr.org/2003/12/the-one-number-you-need-to-grow
Moving Beyond NPS, Medium, https://link.medium.com/OHO1Mz6IGY
Hubspot, The ultimate guide to your Net Promoter Score (NPS)
More on the Marketing Canvas
Marketing Canvas - Pains and Gains
The Pains and Gains sub-dimension in the Marketing Canvas focuses on identifying the constraints (pains) that block your customers from solving their problems and the delights (gains) that you can provide by addressing these constraints. By thoroughly understanding the pain points and potential gains, businesses can deliver solutions that resonate with customer needs and create a more positive overall experience.
Last update: 23/10/2024
The final edits focus on reviewing the scoring system and refining the Green Clean example.
In a nutshell
The Pains and Gains sub-dimension in the Marketing Canvas focuses on identifying the constraints (pains) that block your customers from solving their problems and the delights (gains) that you can provide by addressing these constraints. By thoroughly understanding the pain points and potential gains, businesses can deliver solutions that resonate with customer needs and create a more positive overall experience.
For example, Green Clean customers may experience pain from the use of harmful cleaning chemicals and the difficulty of finding eco-friendly options, but their gain would be the peace of mind that comes from knowing their home is clean and safe for both their family and the environment.
In the Marketing Canvas
The Marketing Canvas is a powerful tool for entrepreneurs and non-marketers to build a robust marketing strategy. It consists of six meta-dimensions, each with four sub-dimensions, for a total of 24 sub-dimensions defining your Marketing Strategy. One of these sub-dimensions is PAINS & GAINS, which falls under the CUSTOMER meta-dimension.
Introduction
The Pains and Gains sub-dimension is part of the Customer category in the Marketing Canvas. It focuses on understanding the constraints or barriers customers face when trying to accomplish their goals and the delights or positive outcomes they seek from resolving these pains. Identifying these elements helps businesses craft offerings that directly target customer frustrations while delivering satisfying results.
What is « pains & gains » ?
Pains are the blockers or frustrations that customers encounter when trying to achieve their goals. These pains can range from emotional concerns to practical obstacles that prevent progress.
Gains, on the other hand, represent the positive outcomes customers wish to achieve, including functional results (like efficiency or ease) and emotional or societal rewards (like feeling aligned with a cause or living up to their values).
For example, Green Clean customers may experience the following:
Pains: Concerns over the health risks of traditional cleaning products, or the frustration of spending too much time cleaning.
Gains: The peace of mind that comes from using eco-friendly products, or the satisfaction of contributing to a healthier environment.
Tools for Identifying Pains & Gains
Identifying your customer's Pains & Gains isn't a guessing game. Several tools and techniques can help you uncover these insights:
Customer Interviews & Surveys: Directly asking your customers about their experiences, frustrations, and delights related to your product or service is a simple yet effective way to identify Pains & Gains.
Focus Groups: This research method allows for an in-depth understanding of customer's perspectives. Hearing customers discuss their experiences can reveal Pains & Gains you might not have considered.
Customer Journey Mapping: This tool visualizes the process a customer goes through to achieve their JTBD, helping you identify potential Pains & Gains at each step.
Social Media Listening: Monitoring social media conversations about your brand or industry can yield insights into common complaints (Pains) and praises (Gains).
Feedback Analysis: Regularly review feedback from support tickets, product reviews, or any other customer touchpoint. This feedback often directly highlights Pains & Gains.
Let’s consider our example of Green Clean. Through a customer survey, Green Clean discovers that many customers are frustrated by the lack of clear instructions on how to responsibly dispose of the product packaging (a Pain). On the other hand, they find that customers appreciate the fresh, natural scent of their products (a Gain).
Translating Pains & Gains into Action
Addressing the pains that prevent customers from achieving their goals while also providing the gains they desire requires a comprehensive approach. Empathize with your customers’ experiences and remove the barriers standing in their way while ensuring your solutions offer clear benefits.
Questions to consider:
What constraints block your customers from solving their problems?
What annoys your customers during their interaction with your product or service?
What could delight your customers and turn their experience into something positive?
How can you measure your customers' engagement with sustainability goals?
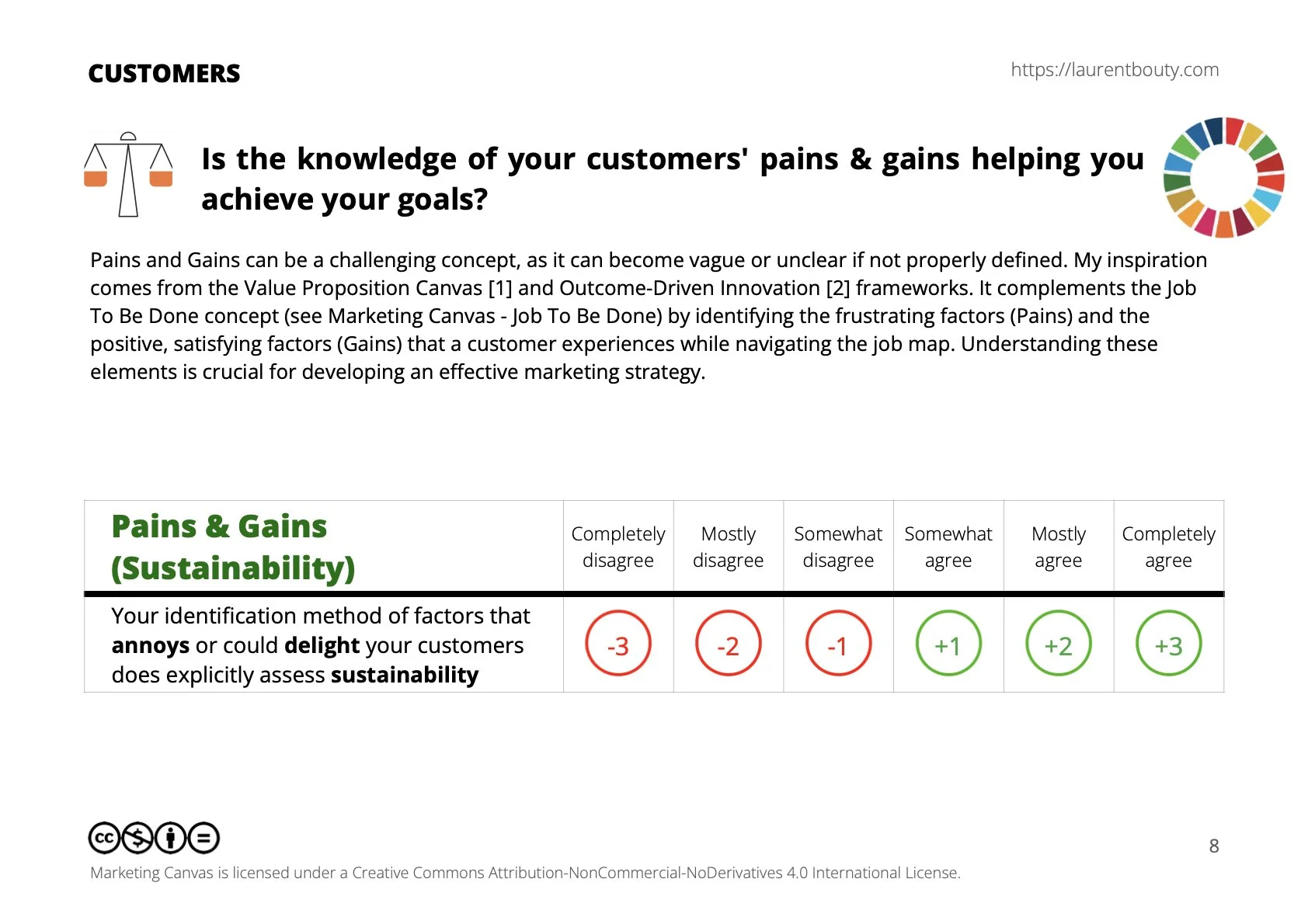
Statements for self-assessment
For a comprehensive evaluation of your understanding and application of the Pains and Gains concept, rate your agreement with the following statements on a scale from -3 (completely disagree) to +3 (completely agree):
You have clearly identified constraints blocking your customer from solving their problem and feel comfortable addressing them.
You have clearly identified factors that annoy your customer during the job map and feel comfortable addressing them.
You have clearly identified factors that could delight your customer during the job map and feel comfortable addressing them.
Your identification method of factors that annoys or could delight your customers does explicitly assess sustainability. (NEW)
Interpretation of the scores
Negative scores (-1 to -3): A negative score suggests a disconnection in your understanding of the constraints or annoyances your customers face. This indicates a lack of insight into the barriers blocking their progress or the gains they seek, which may lead to ineffective solutions.
A score of zero (0): A neutral score reflects uncertainty or a basic awareness of your customers' pains and gains. While you may recognize that constraints and delights exist, you are not fully addressing them. More research is needed to develop a complete understanding.
Positive scores (+1 to +3): Positive scores indicate a clear and thorough understanding of your customers' constraints and delights. You are confident in identifying and addressing the key pain points and gains, and you have the tools in place to measure customer engagement, especially in areas like sustainability.
Case study: Green Clean’s pains and gains
Misaligned understanding (-3, -2, -1): Green Clean fails to recognize the core constraints or frustrations their customers experience, such as concerns over the environmental impact of cleaning products. As a result, their services fall short of addressing the fundamental needs of their eco-conscious customers.
Surface understanding (0): Green Clean has a partial understanding of customer pain points. While they acknowledge that customers want safer products, they do not fully grasp the extent of the annoyance or frustration customers feel about transparency in ingredients or sustainability claims. This limits their ability to fully delight their customers.
Deep understanding (+1, +2, +3): Green Clean deeply understands both the constraints their customers face and the gains they seek. They recognize that their customers are concerned about using harmful chemicals and value transparency, eco-friendliness, and health. By addressing these constraints and providing clear benefits like peace of mind and environmental contribution, Green Clean fosters a loyal customer base aligned with their values.
Conclusion
Identifying and addressing the pains and gains of your customers is essential for delivering products and services that resonate with them on a deeper level. By focusing on removing the constraints that block progress and delivering meaningful delights, you can create long-lasting customer relationships and positive outcomes that extend beyond functional benefits.
Source
Value Proposition Canvas by Strategyzer, https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/value-proposition-canvas
Outcome-Driven Innovation, Medium, https://jobs-to-be-done.com/outcome-driven-innovation-odi-is-jobs-to-be-done-theory-in-practice-2944c6ebc40e